
Osteoporosis
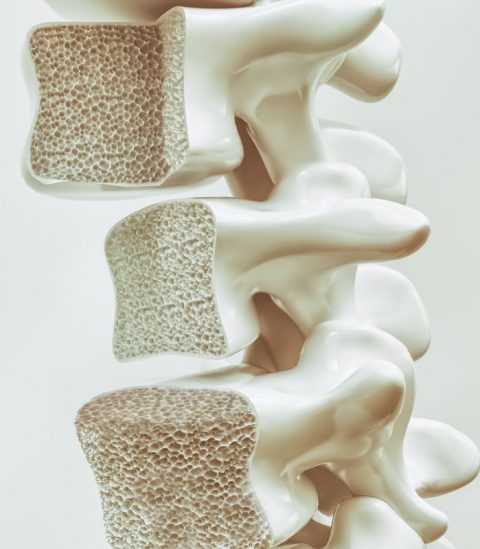
Osteoporosis is a disease where increased bone weakness increases the risk of a broken bone. It is the most common reason for a broken bone among the elderly. Bones that commonly break include the vertebrae in the spine, the bones of the forearm, and the hip. Until a broken bone occurs there are typically no symptoms. Bones may weaken to such a degree that a break may occur with minor stress or spontaneously. Chronic pain and a decreased ability to carry out normal activities may occur following a broken bone.
Osteoporosis is a bone disease that occurs when the body loses too much bone, makes too little bone, or both. As a result, bones become weak and may break from a fall or, in serious cases, from sneezing or minor bumps.
Osteoporosis means “porous bone.” Viewed under a microscope, healthy bone looks like a honeycomb. When osteoporosis occurs, the holes and spaces in the honeycomb are much larger than in healthy bone. Osteoporotic bones have lost density or mass and contain abnormal tissue structure. As bones become less dense, they weaken and are more likely to break. If you’re 50 or older and have broken a bone, ask your doctor or healthcare provider about a bone density test.
- BMD
- Vitamin D
- DEXA
- Novel osteoporotic agents


